Multipurpose Hall Effect Sensor Circuit Circuit Diagram I've decided to upgrade the car with RPM measurement using Hall sensor and a neodymium magnet. In the following steps I'll describe the parts needed for the setup and will provide the code. I also use the IR remote to change speed of the motor (I change the PWM signal +/-20) to check if the code and the setup is working.
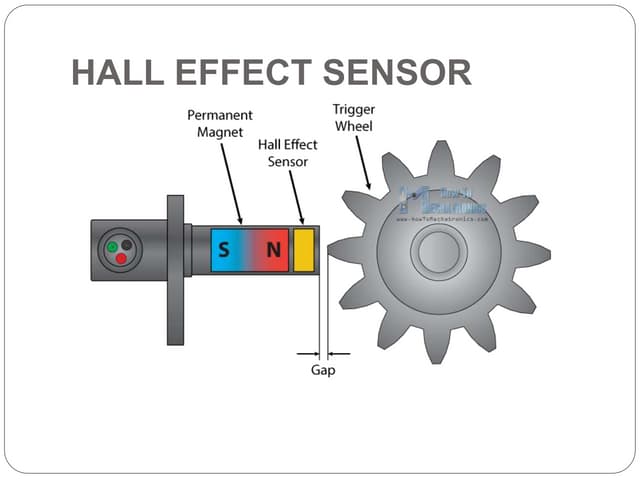
The optical encoder has looser positionning tolerance but requires to be completely in a box to prevent light from seeping in. The hall effect system is more tolerant to harsh environment but a bit harder to setup. With a hall sensor system, you can use a teethed wheel. You can also remove one tooth if you need to detect an absolute position too. Hello, I am trying to measure the speed of a bicycle wheel using a hall effect sensor. I am using the code below and get the RPM which I then convert into m/s. However, I want the measurement to be more accurate. Using my code the RPM changes by 60 which is roughly 2 m/s. I want a more accurate speed measurements with not such big intervals A Hall-effect sensor varies its output voltage in response to a magnetic field. Hall-effect devices are used as proximity sensors and for positioning, The carrier speed is the result of a statistical measure, and non-linear effects of the magnetic field can alter the results obtained experimentally. Therefore, a correction term rh is

Speed measurement with hall effect sensor Circuit Diagram
We will be using the Hall effect sensor and a magnet to find the number of times the car wheel rotated in a minute.The sensor and magnet will be placed in a such a way that at a particular point in every rotation of the wheel the sensor will detect the magnet. One of the draw backs of this code is that the first measurement of speed is
Use the long 5-pin Wireling cable to connect the Hall-Effect Sensor to Port 0 on the Wireling TinyShield. Connect the TinyScreen+ to your computer via the micro USB cable. Step 2: Software Open your Arduino IDE and select the TinyScreen+ from Tools -> Board. Confirm that you are connected to the correct port. 3 Phase BLDC with 3x Hall sensors in 120 degrees, 2 pole-pair; The image below shows the situation: I have setup a timer in XOR mode in the micro. The PSC is [19 - 1] and the Counter Period is [10000 - 1] while the timer clock is 80MHz. My motor has the maximum speed of 3000RPM. The timer is setup in XOR mode and with each transition generates The GND of the sensor is connected to the GND pin on the Arduino. The Vout or signal pin of the Hall effect sensor is connected to the Arduino's interrupt pin (digital pin 2). Furthermore, a 10K resistor is connected between the VCC and Vout pins of the Hall effect sensor. This is done to pull the output of the Hall effect sensor to 5V.
